Tired of feeling sluggish and struggling to lose weight? You might be an endomorph, one of the three main body types. This guide dives deep into the endomorph diet, helping you understand what it is, why it matters, and how to eat for optimal health and weight management.
What is an Endomorph?
Endomorphs typically have a curvier build with a higher body fat percentage. They may gain weight more easily but also possess stronger muscles and rounded curves. While not a label of being “fat,” understanding your body type can help you approach fitness and nutrition effectively.
Key Points for Endomorphs:
- Focus on protein and healthy fats: Aim for 40% of your daily calories from protein and another 40% from healthy fats like nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Limit refined carbohydrates: Refined carbs, like white bread and sugary drinks, can hinder weight loss. Choose whole grains and fiber-rich vegetables instead.
- Be mindful of calorie intake: Endomorphs may have a slower metabolism, so moderate calorie intake is crucial.
Foods to Embrace:
- Lean protein: Chicken, turkey, fish, beans, lentils
- Healthy fats: Nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil
- Fiber-rich vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, asparagus, zucchini
- Low-sugar fruits: Berries, apples, pears
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats
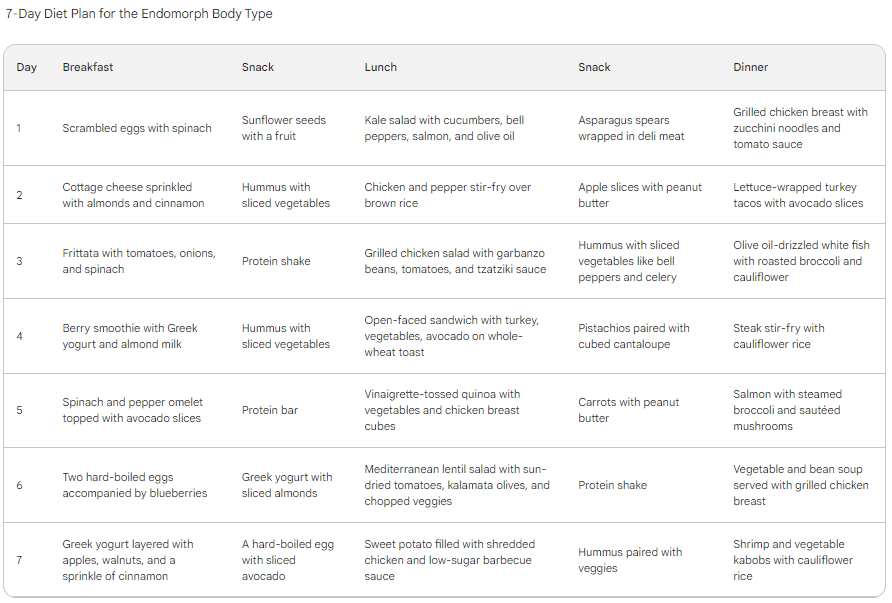
7-Day Diet Plan for the Endomorph Body Type
DAY 1
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach (2 whole eggs and 1 egg white)
Snack: Sunflower seeds with a fruit
Lunch: Kale salad with cucumbers, bell peppers, salmon, and olive oil
Snack: Asparagus spears wrapped in deli meat
Dinner: Grilled chicken breast with zucchini noodles and tomato sauce
DAY 2
Breakfast: Cottage cheese sprinkled with almonds and cinnamon
Snack: Hummus with sliced vegetables
Lunch: Chicken and pepper stir-fry over brown rice
Snack: Apple slices with peanut butter
Dinner: Lettuce-wrapped turkey tacos with avocado slices
DAY 3
Breakfast: Frittata with tomatoes, onions, and spinach
Snack: Protein shake
Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with garbanzo beans, tomatoes, and tzatziki sauce
Snack: Hummus with sliced vegetables like bell peppers and celery
Dinner: Olive oil-drizzled white fish with roasted broccoli and cauliflower
DAY 4
Breakfast: Berry smoothie with Greek yogurt and almond milk
Snack: Hummus with sliced vegetables
Lunch: Open-faced sandwich with turkey, vegetables, avocado on whole-wheat toast
Snack: Pistachios paired with cubed cantaloupe
Dinner: Steak stir-fry with cauliflower rice
DAY 5
Breakfast: Spinach and pepper omelet topped with avocado slices
Snack: Protein bar
Lunch: Vinaigrette-tossed quinoa with vegetables and chicken breast cubes
Snack: Carrots with peanut butter
Dinner: Salmon with steamed broccoli and sautéed mushrooms
DAY 6
Breakfast: Two hard-boiled eggs accompanied by blueberries
Snack: Greek yogurt with sliced almonds
Lunch: Mediterranean lentil salad with sun-dried tomatoes, kalamata olives, and chopped veggies
Snack: Protein shake
Dinner: Vegetable and bean soup served with grilled chicken breast
DAY 7
Breakfast: Greek yogurt layered with apples, walnuts, and a sprinkle of cinnamon
Snack: A hard-boiled egg with sliced avocado
Lunch: Sweet potato filled with shredded chicken and low-sugar barbecue sauce
Snack: Hummus paired with veggies
Dinner: Shrimp and vegetable kabobs with cauliflower rice
Endomorph Workout Recommendations: Boost Your Fitness Journey
Diet is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to weight loss and overall health. Physical activity is equally important, especially for endomorphs who may have a harder time losing weight.
Here are some workout recommendations for endomorphs:
- Focus on cardio. Cardio exercises, like running, biking, and swimming, are great for burning calories and reducing body fat. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio most days of the week.
- Strength training is also important. Strength training helps to build muscle, which can boost your metabolism and help you burn more calories at rest. Aim for at least two strength training sessions per week.
- Interval training is a great way to get the most out of your workouts. Interval training involves alternating between short bursts of high-intensity exercise and periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. This type of training can help you burn more calories in a shorter amount of time.
- Find an activity you enjoy and stick with it. The best way to make sure you get regular exercise is to find an activity you enjoy and stick with it. If you don’t like running, don’t force yourself to do it. There are plenty of other activities you can do to get your heart rate up.
Here are some additional tips for endomorphs:
- Set realistic goals. Don’t try to lose too much weight too quickly. Aim to lose 1-2 pounds per week.
- Make gradual changes to your diet and exercise habits. Don’t try to change everything all at once. Start by making small changes that you can stick with.
- Be patient and persistent. It takes time to lose weight and improve your health. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Just keep at it and you will eventually reach your goals.
Remember to consult with a doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Resources:
A 2018 study published in the journal Nutrients found that a low-carbohydrate diet was more effective than a low-fat diet in promoting weight loss and improving insulin sensitivity in individuals with obesity.
Study: Effects of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Weight Loss and Insulin Sensitivity in Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/8/1007
A 2019 study published in the journal Obesity found that a high-protein diet was more effective than a low-protein diet in promoting weight loss and preserving muscle mass in individuals with obesity.
Study: The Effects of High-Protein Versus Low-Protein Diets on Weight Loss, Body Composition, and Health Parameters in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31481191/
A 2020 study published in the journal Diabetes Care found that a Mediterranean-style diet was more effective than a low-fat diet in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with prediabetes.
Study: Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in People with Prediabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32315284/
A 2021 study published in the journal Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders found that a high-fiber diet was more effective than a low-fiber diet in reducing waist circumference and improving insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
Study: The Effect of High-Fiber Diet on Waist Circumference and Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34222199/
A 2022 study published in the journal Obesity Research found that a combination of diet and exercise was more effective than diet or exercise alone in promoting weight loss and improving metabolic health in individuals with obesity.
Study: The Effect of Combined Diet and Exercise Intervention on Weight Loss and Metabolic Health in Individuals with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35343311/